Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Penumbra Visualized#
Visualizing the penumbra and umbra of the Earth’s shadow.
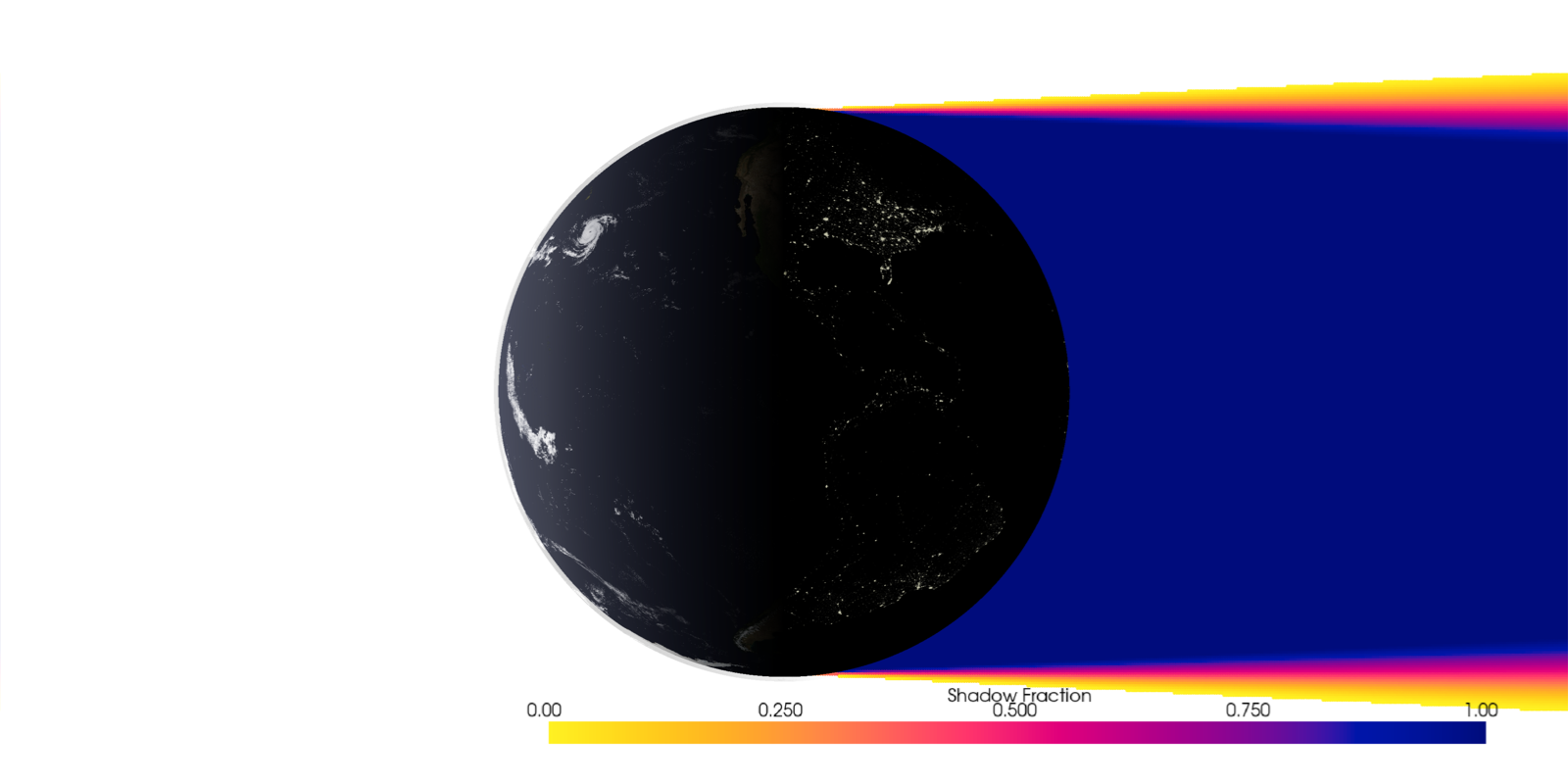
Elapsed time: 1.75e+00 seconds
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import mirage as mr
import mirage.vis as mrv
date = mr.utc(2022, 12, 21)
glim = 80e3
dim = 3000
grid_space = np.linspace(-glim, glim, dim)
gxx, gzz = np.meshgrid(grid_space, grid_space)
rotm = mr.eci_to_sun_ec(date)
gpts = np.vstack((gxx.flatten(), 0 * gxx.flatten(), gzz.flatten())).T
gpts = gpts @ rotm.squeeze()
mr.AstroConstants.sun_r_eq *= 10
mr.tic()
f_shadow = 1 - mr.sun_irradiance_fraction(date, gpts)
mr.toc()
pl = pv.Plotter(window_size=(1600, 800))
mrv.plot_earth(pl, date=date)
mrv.scatter3(
pl,
gpts,
scalars=f_shadow,
point_size=8,
lighting=False,
cmap='bmy_r',
opacity=(f_shadow > 0) * 1,
scalar_bar_args={'title': 'Shadow Fraction'},
)
pl.view_xz()
pl.camera.up = np.array([0, 0, -1]) @ rotm.squeeze()
pl.camera.position = np.array([0e3, -40e3, 0]) @ rotm.squeeze()
# shift = np.array([-30e4, 0, 0]) @ rotm.squeeze()
# pl.camera.position += shift
# pl.camera.focal_point += shift
pl.camera.zoom(1.2)
pl.set_background('white')
# pl.disable_parallel_projection()
pl.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.965 seconds)
