Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Solar System#
Plotting the solar system planet directions with respect to the Earth at a given time
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import mirage as mr
import mirage.vis as mrv
date = mr.now()
fcns = np.array(
[
mr.mercury,
mr.venus,
mr.mars,
mr.jupiter,
mr.saturn,
mr.uranus,
mr.neptune,
mr.moon,
mr.sun,
mr.pluto,
]
)
labels = np.array(
[
'Mercury',
'Venus',
'Mars',
'Jupiter',
'Saturn',
'Uranus',
'Neptune',
'Moon',
'Sun',
'Pluto',
]
)
r = np.zeros((len(fcns), 3))
for i, fcn in enumerate(fcns):
r[i, :] = fcn(date)
pl = pv.Plotter()
mrv.plot_earth(pl, date=date, lighting=False)
mag = 20000
planet_dirs = mr.hat(r)
for pi, labeli in zip(planet_dirs, labels):
mrv.plot_arrow(
pl,
np.zeros(3),
pi,
color='lime',
label=labeli,
name=labeli,
scale=mag * 0.8,
font_size=15,
)
grid = mrv.celestial_grid()
mrv.plot3(
pl,
mag * grid,
color='cornflowerblue',
line_width=5,
lighting=False,
opacity=0.2,
)
mrv.orbit_plotter(pl)
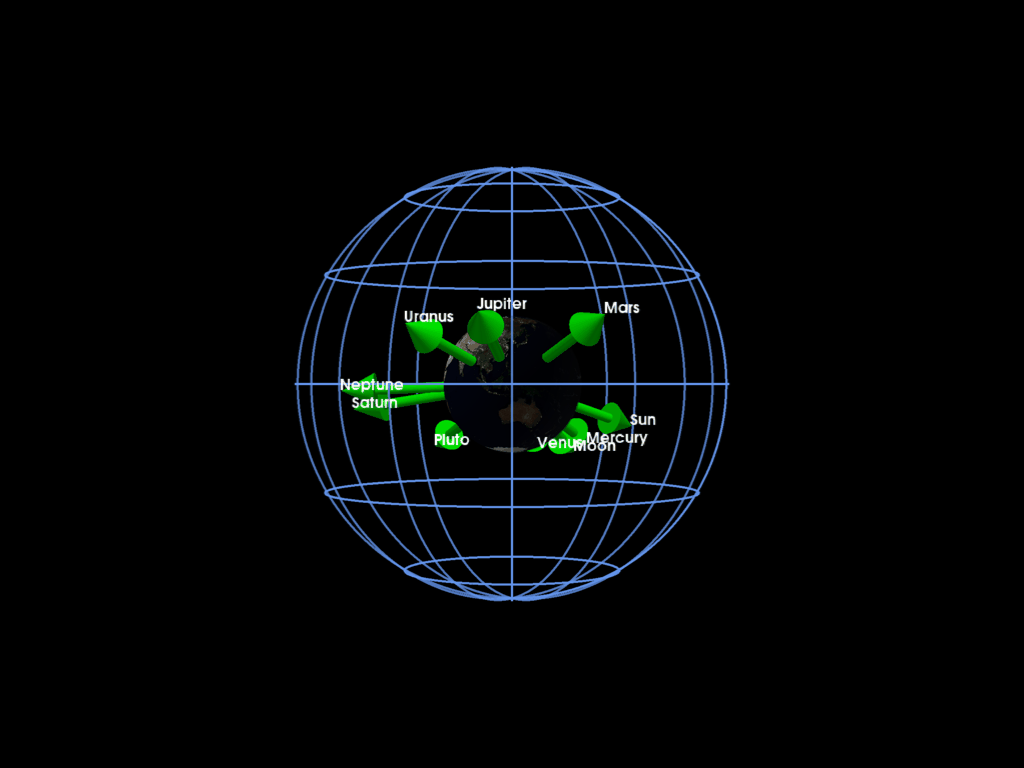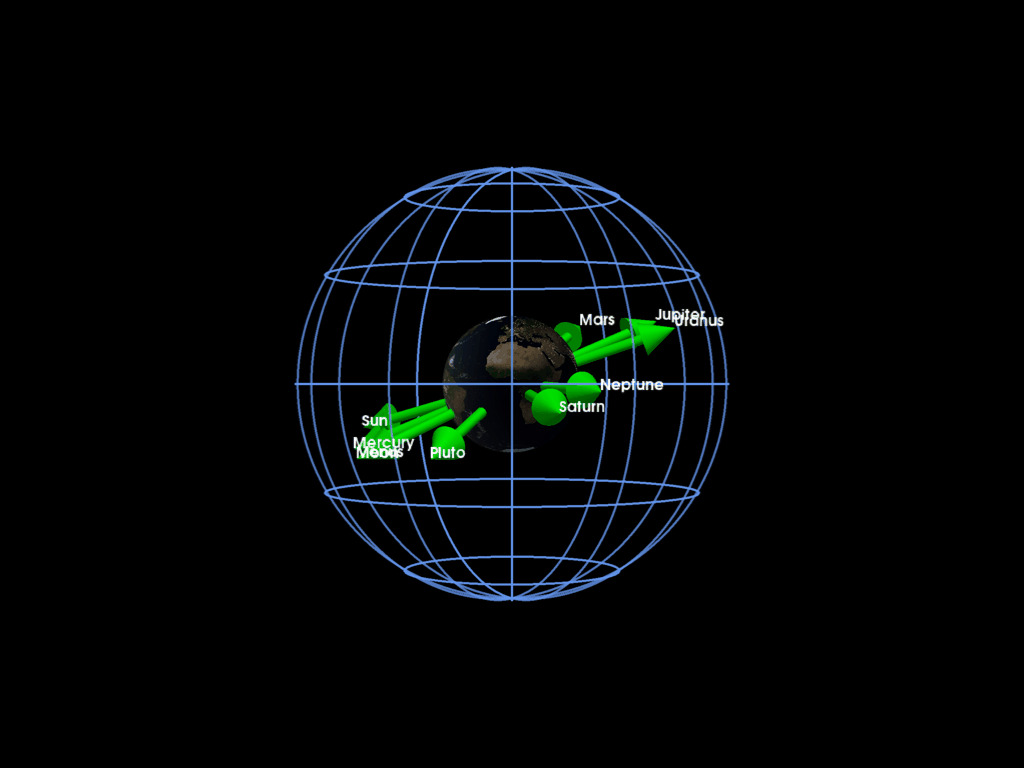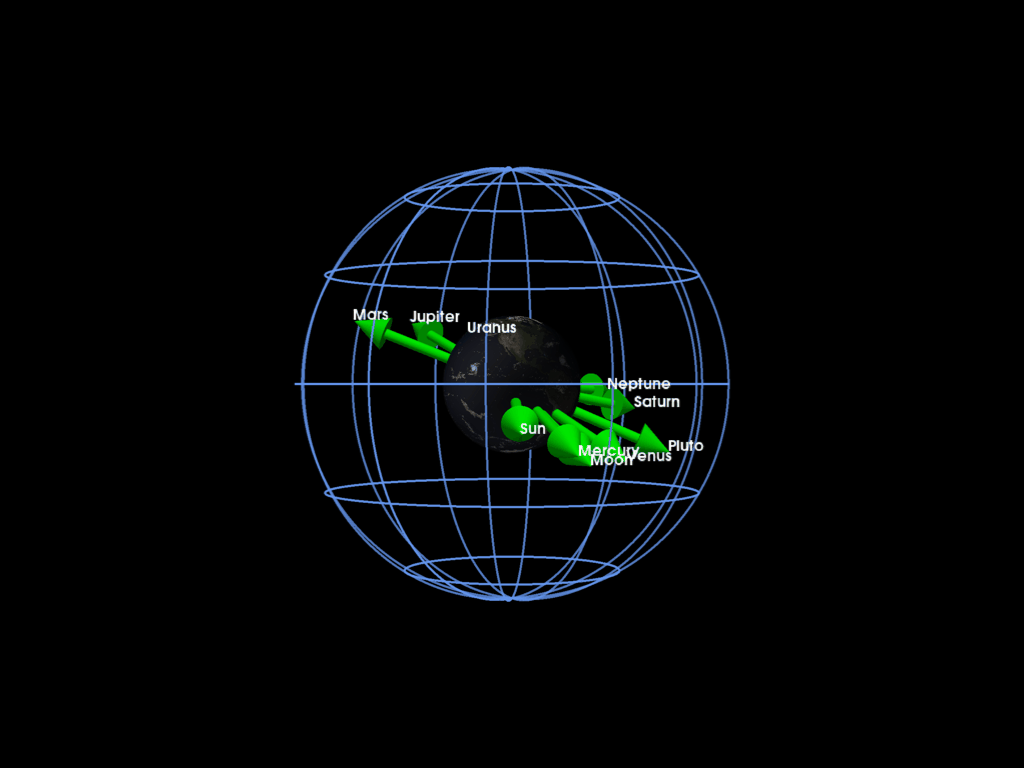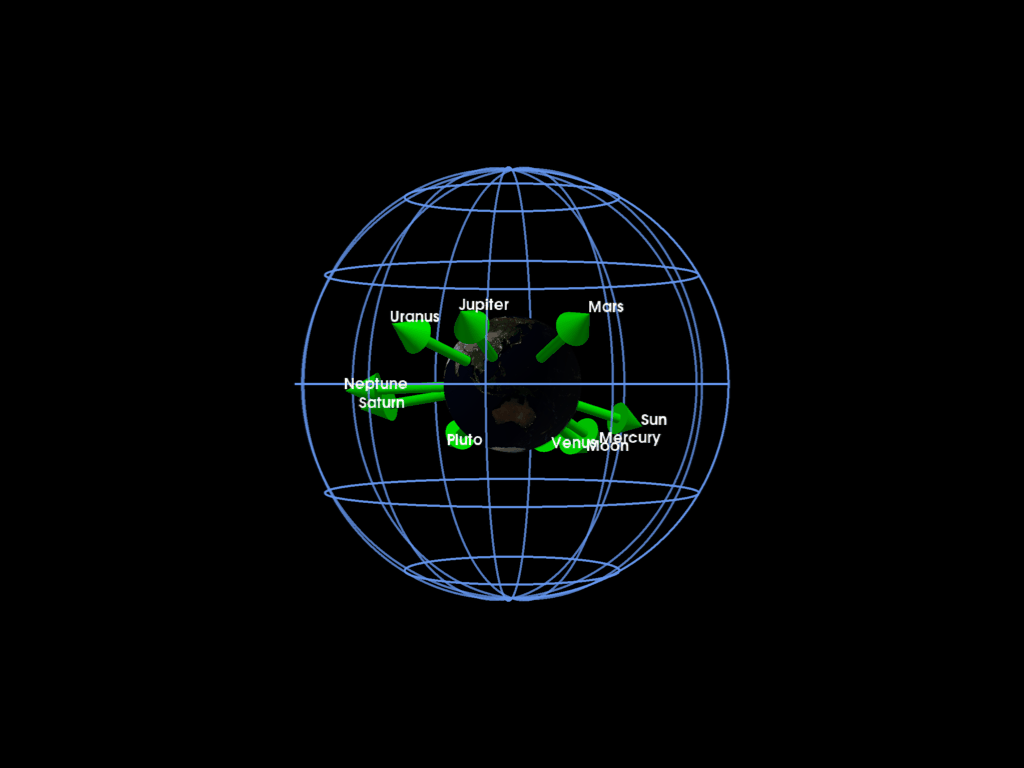
We can also plot the whole solar system by using SPICE interpolation
bodies = np.array(
[
'Mercury',
'Venus',
'Mars',
'Jupiter',
'Saturn',
'Uranus',
]
)
periods = mr.days(
np.array([87.97, 224.7, 686.98, 4332.589, 10759.22, 30688.5, 60182, 90560])
)
r_all = []
for body, period in zip(bodies, periods):
print(body)
dates, epsecs = mr.date_linspace(date, date + period, 100, return_epsecs=True)
fine_dates, fine_epsecs = mr.date_linspace(
dates[0], dates[-1], dates.size * 10, return_epsecs=True
)
r_all.append(mr.SpiceInterpolator(body, fine_dates)(fine_epsecs))
Mercury
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.308 seconds)
