Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
PRNG Speed#
Benchmarking the speed of various numpy pseudorandom number generators
from timeit import timeit
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
from numba import njit
import mirage as mr
n = 4096**2 # the number of pixels in our CCD image
mus = np.random.randint(100, 100000, size=n).reshape(-1, 16)
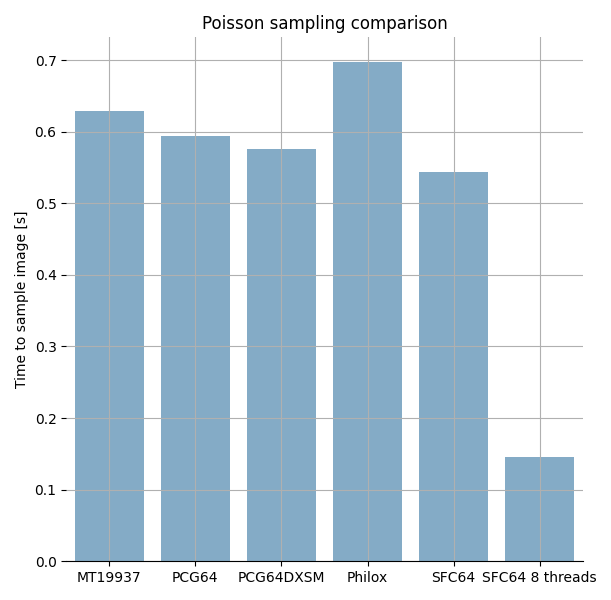
Poisson PRNG
names = ['MT19937', 'MT19937', 'PCG64', 'PCG64DXSM', 'Philox', 'SFC64']
gens = [np.random.Generator(getattr(np.random, n)()).poisson for n in names]
gens.append(mr.multithreaded_poisson)
names.append('SFC64 8 threads')
data = {'dt': [], 'name': []}
for i, (gen, name) in enumerate(zip(gens, names)):
mr.tic()
samples = gen(mus)
dt = mr.toc(return_elapsed_seconds=True)
if i > 0:
data['dt'].append(dt)
data['name'].append(name)
g = sns.catplot(
data=pd.DataFrame(data),
kind='bar',
x='name',
y='dt',
errorbar='sd',
alpha=0.6,
height=6,
)
g.despine(left=True)
g.set_axis_labels('', 'Time to sample image [s]')
g.legend.set_title('')
plt.title('Poisson sampling comparison')
plt.grid()
g.despine(left=True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
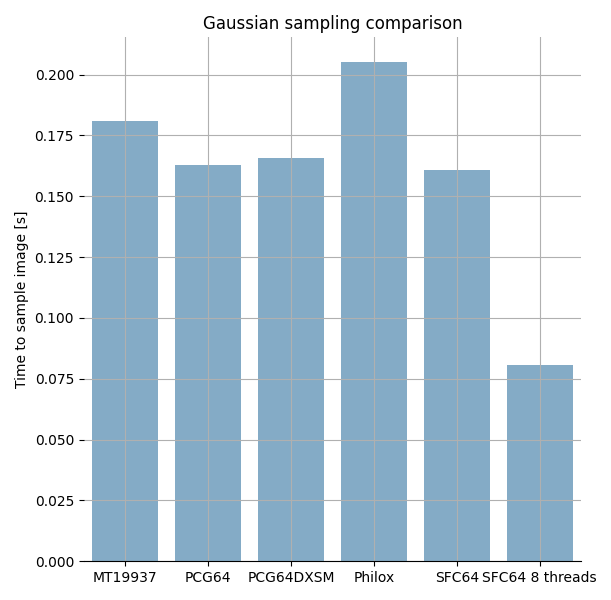
Gaussian PRNG
mus = np.random.randn(n).reshape(-1, 16)
sigmas = np.abs(np.random.randn(n).reshape(-1, 16))
names = ['MT19937', 'MT19937', 'PCG64', 'PCG64DXSM', 'Philox', 'SFC64']
gens = [np.random.Generator(getattr(np.random, n)()).normal for n in names]
gens.append(mr.multithreaded_gaussian)
names.append('SFC64 8 threads')
data = {'dt': [], 'name': []}
for i, (gen, name) in enumerate(zip(gens, names)):
mr.tic()
samples = gen(mus, sigmas)
dt = mr.toc(return_elapsed_seconds=True)
if i > 0:
data['dt'].append(dt)
data['name'].append(name)
g = sns.catplot(
data=pd.DataFrame(data),
kind='bar',
x='name',
y='dt',
errorbar='sd',
alpha=0.6,
height=6,
)
g.set_axis_labels('', 'Time to sample image [s]')
g.legend.set_title('')
plt.title('Gaussian sampling comparison')
plt.grid()
g.despine(left=True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Numba for sampling normals faster
bit_gen = np.random.SFC64()
next_d = bit_gen.cffi.next_double
state_addr = bit_gen.cffi.state_address
@njit
def normals_numba(n, state):
out = np.empty(n)
for i in range((n + 1) // 2):
x1 = 2.0 * next_d(state) - 1.0
x2 = 2.0 * next_d(state) - 1.0
r2 = x1 * x1 + x2 * x2
while r2 >= 1.0 or r2 == 0.0:
x1 = 2.0 * next_d(state) - 1.0
x2 = 2.0 * next_d(state) - 1.0
r2 = x1 * x1 + x2 * x2
f = np.sqrt(-2.0 * np.log(r2) / r2)
out[2 * i] = f * x1
if 2 * i + 1 < n:
out[2 * i + 1] = f * x2
return out
n = 4096**2
def numbacall():
return normals_numba(n, state_addr)
rg = np.random.Generator(bit_gen)
def numpycall():
return rg.normal(size=n)
# Check that the functions work
r1 = numbacall()
r2 = numpycall()
assert r1.shape == (n,)
assert r1.shape == r2.shape
t1 = timeit(numbacall, number=3)
print(f'{t1:.2f} secs for {n} PCG64 (Numba/SFC64) gaussian randoms')
t2 = timeit(numpycall, number=3)
print(f'{t2:.2f} secs for {n} PCG64 (NumPy/SFC64) gaussian randoms')
0.81 secs for 16777216 PCG64 (Numba/SFC64) gaussian randoms
0.22 secs for 16777216 PCG64 (NumPy/SFC64) gaussian randoms
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 10.537 seconds)
