Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
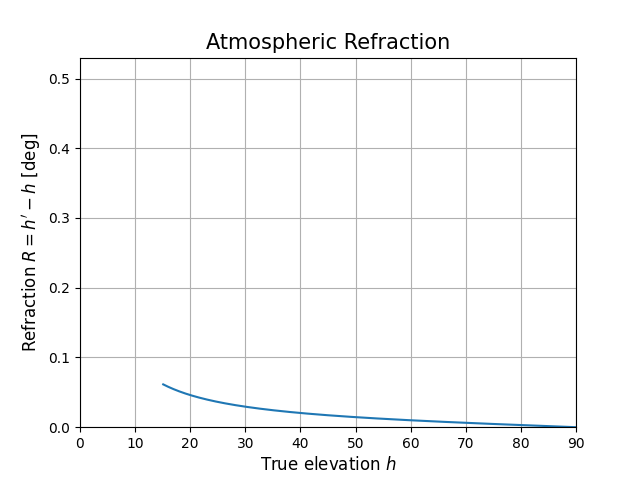
Atmospheric Refraction#
Computing the effect of atmospheric refraction on observations
True elevation: 55.7 deg
Apparent elevation: 55.71173209771628 deg
Refraction: 42.23555177859453 arcsec
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import mirage as mr
import mirage.vis as mrv
true_el = np.deg2rad(np.linspace(15.1, 90, int(1e3)))
atmos_pressure = 1028.4463393 # mbar
atmos_temp = 277.594 # Kelvin
apparent_el = mr.apparent_refacted_elevation(atmos_pressure, atmos_temp, true_el)
test_el_deg = 55.7
test_el_rad = np.deg2rad(test_el_deg)
app_el_deg = np.rad2deg(
mr.apparent_refacted_elevation(atmos_pressure, atmos_temp, test_el_rad)
)
delta_el_deg = app_el_deg - test_el_deg
delta_el_arcsec = delta_el_deg * 3600
print(f'True elevation: {test_el_deg} deg')
print(f'Apparent elevation: {app_el_deg} deg')
print(f'Refraction: {delta_el_arcsec} arcsec')
plt.plot(np.rad2deg(true_el), np.rad2deg(apparent_el - true_el))
mrv.texit(
'Atmospheric Refraction', 'True elevation $h$', "Refraction $R = h' - h$ [deg]"
)
plt.xlim(0, 90)
plt.ylim(0, 0.53)
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 0.137 seconds)
